UV LED Large Area Sources with high irradiance
1540Air-cooled UV-LED array with high intensity for small area curing
View detailsSearch the whole station
UV curing is a versatile and efficient method widely used in various industries, from manufacturing to printing and beyond. One critical aspect that significantly influences the success of UV curing processes is selecting the right wavelength. The appropriate wavelength ensures optimal curing performance and overall efficiency in the application. In this guide, we’ll explore the factors to consider when choosing the right wavelength for UV curing.
Understanding the Basics:
UV curing involves the use of ultraviolet light to initiate a chemical reaction that transforms liquid or gel-like substances into solid materials. The wavelength of the UV light plays a crucial role in determining the effectiveness of this curing process. Wavelength is measured in nanometers (nm), and UV light is typically categorized into UVA (320-400 nm), UVB (280-320 nm), and UVC (200-280 nm).
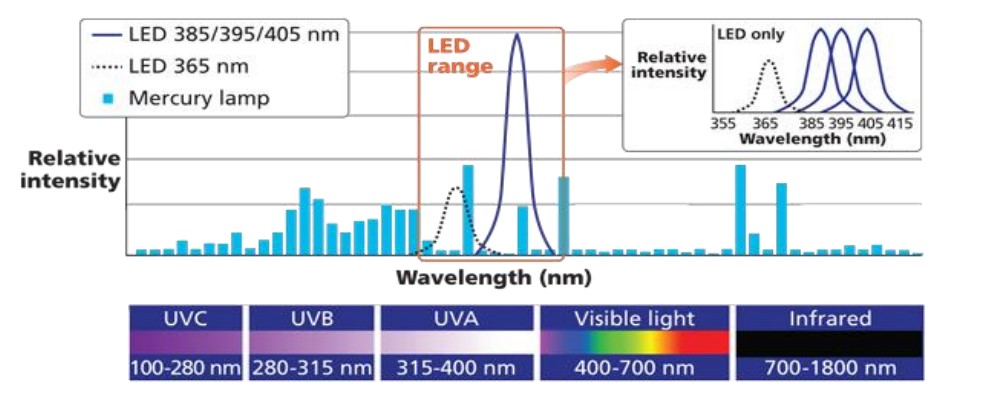
Consider the Material:
Different materials respond best to specific UV wavelengths. It’s essential to consider the photosensitivity of the material being cured. For instance, some materials cure more efficiently under shorter wavelengths, while others require longer wavelengths for optimal results. Understanding the chemistry of the material and its response to different UV wavelengths is fundamental in making the right choice.
Application Requirements:
The intended application also plays a significant role in wavelength selection. For tasks like printing, coating, or bonding, the choice of UV wavelength can impact curing speed, adhesion strength, and the overall quality of the cured product. High-energy wavelengths might be suitable for rapid curing in some applications, while lower-energy wavelengths may be more appropriate for heat-sensitive substrates.
UV Lamp Type:
The type of UV lamp used in the curing process is closely tied to wavelength selection. Different lamps emit UV light at specific wavelengths, and the choice between broad-spectrum lamps and LED lamps can influence the available wavelengths for curing. LED lamps, for example, often offer a narrower and more precise wavelength output compared to traditional broad-spectrum lamps.

Consider Safety Concerns:
While selecting the optimal wavelength for curing, it’s crucial to consider safety implications. Some shorter UV wavelengths, especially UVC, can pose potential health risks to operators. Ensuring that the chosen wavelength aligns with safety standards and guidelines is paramount. Additionally, taking precautions such as using personal protective equipment (PPE) and implementing safety controls in the curing system contributes to a secure working environment.
Testing and Optimization:
Before committing to a specific UV wavelength for a particular application, it’s advisable to conduct thorough testing and optimization. Small-scale trials allow for the assessment of curing efficiency, material compatibility, and overall performance under different wavelengths. This empirical approach ensures that the chosen wavelength aligns with the specific requirements of the application.
Conclusion:
Choosing the right wavelength in UV curing is a nuanced process that demands consideration of material properties, application requirements, and safety concerns. A thorough understanding of these factors, coupled with careful testing and optimization, will lead to the selection of an optimal UV wavelength for your specific curing needs. By making informed decisions, operators can enhance the efficiency, quality, and safety of UV curing processes across diverse applications.
Reach out to our Application Engineering team for additional assistance in utilizing UV/Visible and LED light-curing systems.
Air-cooled UV-LED array with high intensity for small area curing
View detailsinner ring UV LED curing light source are widely used in industrial applications, providing fast and efficient curing for a range of materials
View detailscustomized uv led curing systems can be designed to fit a wide range of applications and workpieces. Whether it's a flat surface, a curved shape, or a complex three-dimensional structure, customised UV curing lights can be tailored to fit the uniq...
View details
HelloPlease log in